Eucalypts: Eucalypt Leaf (TS)
Shown is a transverse section of a eucalypt leaf.
Locate the palisade mesophyll, which has cells with numerous chloroplasts containing chlorophyll,
and is the main photosynthetic tissue.
You can see that palisade mesophyll is symmetrically distributed in the leaf. This
sclerophyllous
leaf does not have a distinct upper and lower surface like
dorsiventral
leaves, but has two identical sides. Such
anatomical
structure is called
isobilateral
, and leaves with this structure are termed
isobilateral leaves.
Eucalypt leaves are firm and leathery. Note the thick walls of many of the cells.
Such thick secondary cell walls consist not only of cellulose, but compounds such as
lignin, the main component of wood.
Lignin
is a polyphenol and is stained blue in this section.
See if you can identify any other structures that are found on both sides of the leaf.
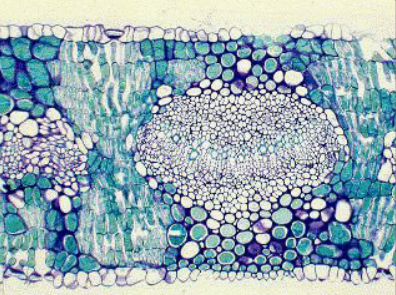
Move the mouse over the section to view these structural features:
Palisade mesophyll
Vascular tissue
Phloem tissue
Sclerenchyma cells
Epidermis
Sub-stomatal cavity
Xylem tissue
A stomate (stomata)
Spongy mesophyll
Subsidiary cells of the stomata
