Specialised Roots: Mycorrhizal Types
Endomycorrhizae form peletons or arbuscules within the cortical cells of the host plant's roots.
Although these do not penetrate the cell membrane, they greatly increase its surface area and,
therefore, the area of contact between the fungus and its host.
There are two main types of endomycorrhizae: orchid (characteristic of the family Orchidaceae and formed by basidiomycete fungi)
and vesicular-arbuscular or VA (common to many plant families and formed by zygomycete fungi).
VA mycorrhizae are particularly effective at solubilising and transferring phosphorus to the host plant.
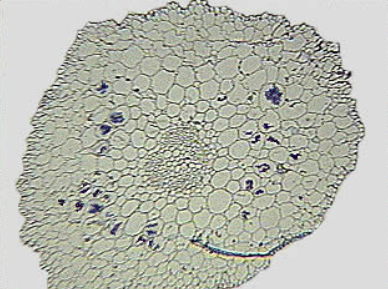
Thin cross-section of a mycorrhizal orchid root.
Move the mouse over the different tissues of the section...
Roots cortex
Fungal peletons
Vascular cylinder
